Andy Roddick has Mono

American professional tennis player Andy Roddick, 27, has been wondering why his game has slipped this summer. The top ranked US, and former World No. 1 player has suffered a number of uncharacteristic losses. He felt more tired this summer, and couldn’t keep up with his usual workout routine. This Saturday, Roddick reported that one of several blood tests came back positive for mononucleosis. Doctors thought he had probably had the disease for a few months, and it was now nearly over. Roddick told the Associated Press:
“I’m just glad that we found out something that was causing it. It’s weird, the fear of kind of the unknown and not knowing what’s going on. There were some days where it was good, and some days where it was real bad. So it was like you would have one of those two or three good days, and it was like, ‘OK, you’re just being kind of a wimp.'”
“So it’s nice to have a little bit of clarity moving forward. It’s not something that’s going to affect me, anything super-serious.”
What is Mononucleosis?
Mononucleosis (or mono, for short) is a viral infection causing fever, sore throat, and swollen lymph glands, especially in the neck. The most common cause is a virus called Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV), but sometimes it is caused by another virus called cytomegalovirus (CMV). It is spread in the saliva and close contact, which is why it is sometimes called the “kissing disease.” However kissing is not the only way that mono can be spread. Drinking from the same glass or using the same utensils as an infected person can also spread the disease. Symptoms begin 4-6 weeks after exposure. Although people of any age can get mono, it is most common in those between the ages of 15 to 35 years old.
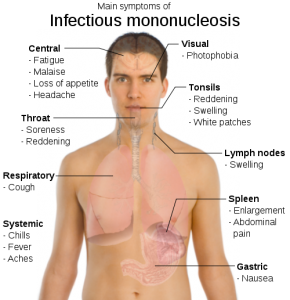
Symptoms of mononucleosis include:
- Drowsiness
- Fever (often high)
- General discomfort, uneasiness, or ill feeling
- Loss of appetite
- Muscle aches or stiffness
- Rash- usually blotchy pink
- Sore throat- especially with swollen tonsils with pus on them
- Swollen lymph nodes, especially in the neck and armpit
- Swollen spleen
Less frequently occurring symptoms include:
- Chest pain
- Cough
- Fatigue
- Headache
- Hives
- Jaundice (yellow color to the skin)
- Neck stiffness
- Nosebleed
- Rapid heart rate
- Sensitivity to light
- Shortness of breath
There is no “cure” for mono- since it is a viral infection, it will go away on it’s own. Treatment is symptomatic- rest, fluids, over-the-counter medications for fever, such as acetominophen or ibuprofen, and using throat lozenges or gargling with salt water for sore throat pain. Antibiotics are not effective in treating mononucleosis.
Symptoms related to mono caused by EBV infection seldom last for more than 4 months. When such an illness lasts more than 6 months, it is frequently called chronic EBV infection. However, laboratory evidence for continued active EBV infection is usually not found in these patients. The illness should be investigated further to determine if it meets the criteria for chronic fatigue syndrome, or CFS- probably a good topic for a future blog.
For more information, click here to be transferred to a Resounding Health casebook on Mononucleosis.
























0 comments