Steven Tyler’s “Lucky to be Alive!”

Steven Tyler seems to be making a major comeback. The Aerosmith frontman has gotten favorable reviews in his new role as American Idol judge, showing a sympathetic, humorous side that few knew was there. He’s on the cover of People magazine this week, had an interview with Today show host Matt Lauer, and will be releasing his memoir Does the Noise in My Head Bother You? on May 3rd. But Tyler says it’s amazing that he has made it this far. As he told People:
“Left up to my own devices, I probably would have been dead several times over.”
It’s well known that Tyler has had drug problems and been in rehab eight times, but he has also had a slew of other health issues. He had a torn ACL ligament in his knee, a broken blood vessel in his throat and, in 2005, was diagnosed with Hepatitis C. Post-surgery pain medications got him addicted to prescription pain medications, and in August 2009 he took a bad tumble off a stage, lacerating his scalp, breaking his left shoulder. This, combined with his kids concerns about his health, prompted his last visit to the Betty Ford Center which has finally kept him clean.
What is hepatitis? (Source: CDC)
“Hepatitis” means inflammation of the liver. The liver is a vital organ that processes nutrients, filters the blood, and fights infections. When the liver is inflamed or damaged, its function can be affected. Hepatitis is most often caused by a virus. In the United States, the most common types of viral hepatitis are Hepatitis A, Hepatitis B, and Hepatitis C. Heavy alcohol use, toxins, some medications, and certain medical conditions can also cause hepatitis.
What is Hepatitis C?
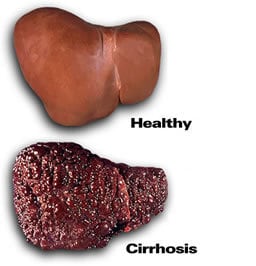
Hepatitis C is a contagious liver disease that results from infection with the Hepatitis C virus. When first infected, a person can develop an “acute” infection, which can range in severity from a very mild illness with few or no symptoms to a serious condition requiring hospitalization. Acute Hepatitis C is a short-term illness that occurs within the first 6 months after someone is exposed to the Hepatitis C virus. For reasons that are not known, 15%–25% of people “clear” the virus without treatment. Approximately 75%–85% of people who become infected with the Hepatitis C virus develop “chronic,” or lifelong, infection. Chronic Hepatitis C is a long-term illness that occurs when the Hepatitis C virus remains in a person’s body. Over time, it can lead to serious liver problems, including liver damage, cirrhosis, liver failure, or liver cancer.
How is Hepatitis C spread?
Hepatitis C is usually spread when blood from a person infected with the Hepatitis C virus enters the body of someone who is not infected. Today, most people become infected with Hepatitis C by sharing needles or other equipment to inject drugs. Before widespread screening of the blood supply began in 1992, Hepatitis C was also commonly spread through blood transfusions and organ transplants. Although uncommon, outbreaks of Hepatitis C have occurred from blood contamination in medical settings.
Can Hepatitis C be spread through sex?
Yes, although scientists do not know how frequently this occurs. Having a sexually transmitted disease or HIV, sex with multiple partners, or rough sex appears to increase a person’s risk for Hepatitis C. There also appears to be an increased risk for sexual transmission of Hepatitis C among gay men who are HIV-positive.
Can a person get Hepatitis C from a tattoo or piercing?
There is little evidence that Hepatitis C is spread by getting tattoos in licensed, commercial facilities. Whenever tattoos or body piercings are given in informal settings or with non-sterile instruments, transmission of Hepatitis C and other infectious diseases is possible.
What are the symptoms of Hepatitis C?
Many people with Hepatitis C do not have symptoms and do not know they are infected. Even though a person has no symptoms, the virus can still be detected in the blood. If symptoms occur with acute infection, they can appear anytime from 2 weeks to 6 months after exposure. Symptoms of acute disease include:
- yellowish eyes and skin, called jaundice
- a longer than usual amount of time for bleeding to stop
- swollen stomach or ankles
- easy bruising
- tiredness
- upset stomach
- fever
- loss of appetite
- diarrhea
- light-colored stools
- dark yellow urine
Symptoms of chronic Hepatitis C can take up to 30 years to develop. Damage to the liver can silently occur during this time. When symptoms do appear, they often are a sign of advanced liver disease:
 yellowish eyes and skin, called jaundice
yellowish eyes and skin, called jaundice- a longer than usual amount of time for bleeding to stop
- swollen stomach or ankles
- tiredness
- nausea
- weakness
- loss of appetite
- weight loss
- spiderlike blood vessels, called spider angiomas, that develop on the skin
How is Hepatitis C treated?
Hepatitis C is not treated unless it becomes chronic. Chronic hepatitis C is treated with drugs that slow or stop the virus from damaging the liver. Chronic hepatitis C is most often treated with the drug combination peginterferon and ribavirin, which attacks the hepatitis C virus. Peginterferon is taken through weekly shots and ribavirin is taken daily by mouth. Treatment lasts from 24 to 48 weeks. Last week an FDA panel recommended approval of a new medication, boceprevir (Victrelis), for the treatment of Hepatitis C. This medication would be added to the above drug combination.
How common is Hepatitis C?
An estimated 3.2 million people in the United States have chronic Hepatitis C. Most are unaware of their infection. Each year, about 17,000 Americans become infected with Hepatitis C. Approximately 12,000 people die every year from Hepatitis C-related liver disease.
Is there a vaccine for Hepatitis C?
Although there is currently no vaccine to prevent Hepatitis C, research is being conducted to develop one.
For more information, click here to go to the Resounding Health Casebook on the topic.



























4 Comments