Homeland’s James Rebhorn Dies of Melanoma
You may not recognize his name, but you certainly would recognize his face: James Rebhorn has been working steadily on television and the big screen for over 30 years.
He’s been seen in Independence Day, Scent of a Woman and Meet the Parents. He was a regular on TV series Big Lake, Enlightened, and White Collar. He was the judge that sentenced Seinfeld and his friends to jail on the series finale. And his most recent role was that of Frank Mathison, Carrie’s father, on the Showtime series Homeland.
The 65-year-old actor died of the skin cancer melanoma. He was first diagnosed with the disease in 1992.
What are the different types of skin cancer ?
Your skin has many purposes. It protects your body from heat, injury, and infection. It also protects your body from damage caused by ultraviolet (UV) radiation (such as from the sun or sunlamps). Your skin stores water and fat. It helps control body heat. Also, your skin makes vitamin D.
Melanoma is one of the three main types of skin cancer, the other two types being basal cell and squamous cell cancers. Each forms from a different cell type within the skin.
The picture shows the two main layers of the skin:
- Epidermis: The epidermis is the top layer of your skin. It’s mostly made of flat cells called squamous cells.
- Below the squamous cells deeper in the epidermis are round cells called basal cells.
- Cells called melanocytes are scattered among the basal cells. They are in the deepest part of the epidermis. Melanocytes make the pigment (color) found in skin. When skin is exposed to UV radiation, melanocytes make more pigment, causing the skin to darken, or tan.
- Dermis: The dermis is the layer under the epidermis. The dermis contains many types of cells and structures, such as blood vessels, lymph vessels, and glands. Some of these glands make sweat, which helps cool your body. Other glands make sebum. Sebum is an oily substance that helps keep your skin from drying out. Sweat and sebum reach the surface of your skin through tiny openings called pores.
Basal cell skin cancer: Basal cell skin cancer begins in the basal cell layer of the skin. It usually occurs in places that have been in the sun. For example, the face is the most common place to find basal cell skin cancer. In people with fair skin, basal cell skin cancer is the most common type of skin cancer.
Squamous cell skin cancer: Squamous cell skin cancer begins in squamous cells. In people with dark skin, squamous cell skin cancer is the most common type of skin cancer, and it’s usually found in places that are not in the sun, such as the legs or feet. However, in people with fair skin, squamous cell skin cancer usually occurs on parts of the skin that have been in the sun, such as the head, face, ears, and neck.
Tell me more about Melanoma…
Melanoma begins in melanocytes (pigment cells). Most melanocytes are in the skin.
Melanoma can occur on any skin surface. In men, it’s often found on the skin on the head, on the neck, or between the shoulders and the hips. In women, it’s often found on the skin on the lower legs or between the shoulders and the hips.
Melanoma is rare in people with dark skin. When it does develop in people with dark skin, it’s usually found under the fingernails, under the toenails, on the palms of the hands, or on the soles of the feet.
Who is at risk for skin cancer and melanoma?
Risks for Any Type of Skin Cancer
Studies have shown that the following are risk factors for the three most common types of skin cancer:
- Sunlight: Sunlight is a source of UV radiation. It’s the most important risk factor for any type of skin cancer. The sun’s rays cause skin damage that can lead to cancer.
- Severe, blistering sunburns: People who have had at least one severe, blistering sunburn are at increased risk of skin cancer. Although people who burn easily are more likely to have had sunburns as a child, sunburns during adulthood also increase the risk of skin cancer.
- Lifetime sun exposure: The total amount of sun exposure over a lifetime is a risk factor for skin cancer.
- Tanning: Although a tan slightly lowers the risk of sunburn, even people who tan well without sunburning have a higher risk of skin cancer because of more lifetime sun exposure.
Sunlight can be reflected by sand, water, snow, ice, and pavement. The sun’s rays can get through clouds, windshields, windows, and light clothing.
Additional risk factors for melanoma:
- Dysplastic nevus: A dysplastic nevus is a type of mole that looks different from a common mole. A dysplastic nevus may be bigger than a common mole, and its color, surface, and border may be different. It’s usually wider than a pea and may be longer than a peanut. A dysplastic nevus can have a mixture of several colors, from pink to dark brown. Usually, it’s flat with a smooth, slightly scaly or pebbly surface, and it has an irregular edge that may fade into the surrounding skin.
A dysplastic nevus is more likely than a common mole to turn into cancer. However, most do not change into melanoma. A doctor will remove a dysplastic nevus if it looks like it might have changed into melanoma.
- More than 50 common moles: Usually, a common mole is smaller than a pea, has an even color (pink, tan, or brown), and is round or oval with a smooth surface. Having many common moles increases the risk of developing melanoma.
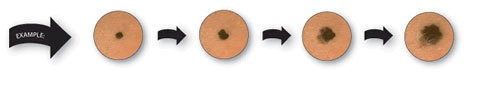
The ABCDEs of Melanoma
 Asymmetry; one half unlike the other half.
Asymmetry; one half unlike the other half.
 Border; irregular, scalloped or poorly defined border.
Border; irregular, scalloped or poorly defined border.
 Color; varied from one area to another; shades of tan and brown, black; sometimes white, red or blue.
Color; varied from one area to another; shades of tan and brown, black; sometimes white, red or blue.
 Diameter; while melanomas are usually greater than 6mm (the size of a pencil eraser) when diagnosed, they can be smaller.
Diameter; while melanomas are usually greater than 6mm (the size of a pencil eraser) when diagnosed, they can be smaller.
 Evolving; a mole or skinl esion that looks different from the rest or is changing in size,shape, or color.
Evolving; a mole or skinl esion that looks different from the rest or is changing in size,shape, or color.
Treatment for skin cancer depends on the type and stage of the disease, the size and place of the tumor, and your general health and medical history. In most cases, the goal of treatment is to remove or destroy the cancer completely. Most skin cancers can be cured if found and treated early.
.



























0 comments